Is Stainless Steel Magnetic?
Magnetic vs. non-magnetic stainless steel: how stainless steel affects magnet strength
1. Are all types of stainless steel magnetic?
Will a magnet stick to stainless steel? It depends on what type of stainless you're using. Some steels are only weakly magnetic, and some are not magnetic at all. Austenitic stainless steels like 304 or 316 stainless are good examples of this.
A ferritic stainless like 430 stainless steel, on the other hand, is ferromagnetic. Magnets stick to it. You might see magnetic forces that are 5-20% weaker compared to low carbon steel.
2. In-depth analysis of magnetic and non-magnetic stainless steel
How much weaker is ferritic stainless steel?
Find out the magnetic strength of ferritic and other types of stainless steel in our detailed video analysis where we do a hands on demonstration of magnet strength on each type of steel.
Shop Mounting Magnets Made for Steel & More
Browse mounting magnets and other magnets made to stick strongly to stainless steel.



3. Magnetic stainless steel FAQ
Below is a collection of commonly asked questions about sticking magnets to stainless steel, differences in steel grades and more.
-
How much weaker is stainless steel?
We tested a few different thicknesses of steel vs. 430 stainless steel. We simulated a lot more. We considered disc magnets of various diameters and thicknesses. The steel it sticks to was always much larger than the magnet diameter, but we varied the thickness. The results varied, yet in all of these scenarios the magnet strength on stainless steel ranged from 82% to 99% of the pull force to regular steel.
As a general rule of thumb, we saw more strength where the stainless steel didn't get saturated, i.e. little magnet to big steel. If the magnet was large and the steel was thin, the magnet pull force was less.
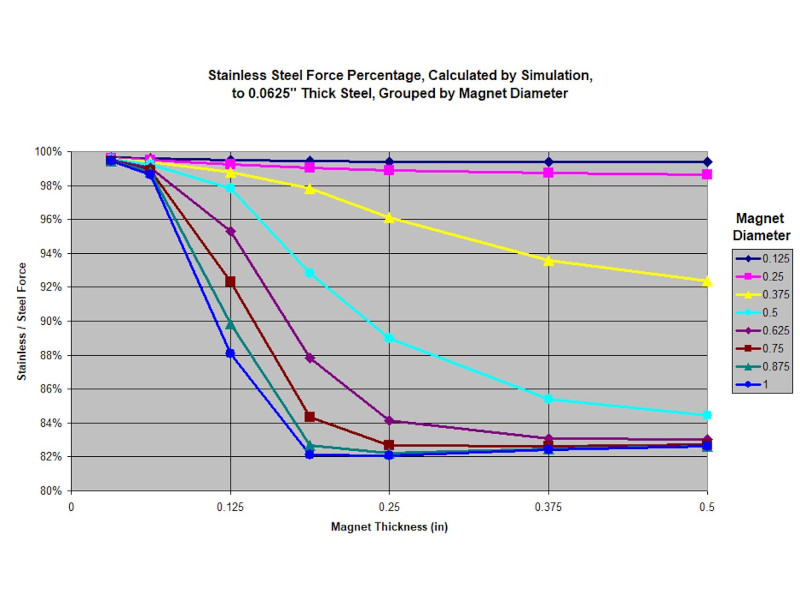
In the graph shown, we simulated a variety of magnet sizes to a 1/16" steel plate. Though the results varied quite a lot depending on the exact geometry, all pull force values were within 82% to 99% of the pull force to a piece of regular low carbon steel.
-
Is all stainless steel magnetic (ferromagnetic)? Will magnets stick to it?
No. It varies depending on the exact stainless steel. We only covered a few in this article. We found:
- 430 Ferritic Stainless Steel: Magnetic
- 304 Austenitic Stainless Steel: Not magnetic, or a little magnetic after cold work (bending, deforming, etc.)
- 316 Austenitic Stainless Steel: Not magnetic.
-
How do I know if my stainless steel is magnetic?
Try it! Finding good magnetic data on all the kinds of steel out there turns out to be surprisingly hard. We picked these three (304, 316, & 430) because they're so common. For some less common varieties, the magnetic specification information can be hard to find, and harder to know if it's trustworthy.
If you're using an odd variety of steel, don't make too many assumptions. Prototype and test!
-
Will stainless steel act as a magnetic shield?
Yes, steel can act as a magnetic shield, however, probably not in the way you are thinking. Magnetic “shields” don't block magnetic fields, they redirect it. Learn more in our Magnetic Shielding article.
All metals that act as good shields are also attracted to magnets. If you're using a stainless steel like 316 that isn't ferromagnetic, it's not blocking any fields, at least not any more than an air gap.
-
Will paint reduce the pull force of a magnet to a piece of stainless steel?
Yes. The magnet is farther away from the steel, by the small distance that's the thickness of the paint. This is true for any ferromagnetic steel, not just stainless steel.
Many questions are answered in the above YouTube video and FAQs, but if still you have any questions about magnets and stainless steel we haven't included, please email us!